What Should You Know Before Buying a Processor?
There are two main processor manufacturers when it comes to computers: AMD and Intel. It's important to know exactly what you want to do with your computer or laptop before choosing either of these options.

Whether you are looking for the best processor for gaming, or one with the power to help you overcome the most demanding workloads. Buying the right processor can be confusing. Cores, threads, clocks, and cache are numbers that we should not be afraid to choose, but understanding them requires a bit of knowledge.
What is a Processor?
A processor, also known as CPU (Central Processing Unit), is the main component of a computer that performs the operations and calculations that allow a computer to function. Some people refer to it as the brain of the computer. Here are some key points about what a processor is and what it does:
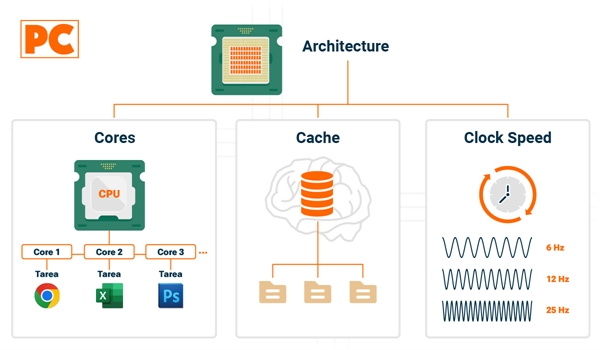
What is the function of a processor?
It executes instructions from programs. This includes everything from the operating system to the applications you use. These instructions can be as simple as adding two numbers or as complex as rendering graphics in real-time in a video game. Among the tasks it performs, we can find:
- Basic Calculations: Arithmetic and logic.
- Input/Output Management: Controls communication with other components like RAM, storage, and peripherals
- Multitasking: Manages multiple tasks at the same time, allocating processing time to each one.
What are the key components of a processor?
- Cores: Cores are the units that actually perform the calculations. Modern processors can have anywhere from one to several cores.
- Cache: High-speed memory that the processor uses to temporarily store data it needs to access quickly.
- Clock Speed: Measured in gigahertz (GHz), it indicates the number of operation cycles the processor can perform per second. More GHz generally means more speed, but efficiency also depends on the architecture.
- Architecture: Refers to how the processor is internally designed, including the layout of cores, the size of the cache, and the manufacturing technology (for example, 7nm, 10nm), which affects its performance and energy efficiency.
What are the key factors to consider before buying a Processor?
When purchasing a processor, there are several key aspects to consider, such as compatibility with the motherboard, the number of cores, clock speed, and overclocking capabilities. However, your choice of processor should not be made in isolation. It's important to think about how it will integrate with the rest of your system.
Before settling on a processor, it would be wise to educate yourself about other devices that are equally crucial for your system's overall performance. For instance, What Should You Know Before Buying a Computer? This article provides a comprehensive overview of the factors you should consider when selecting a computer, helping you ensure that the processor you choose fits your needs perfectly.
If your focus is on a laptop, we recommend reading What Should You Know Before Buying a Laptop? This blog offers valuable information on the features to look for in a laptop, ensuring that all the pieces of the puzzle work together seamlessly.
When considering buying a processor, several key factors should guide your decision to ensure you get the best performance and compatibility with your needs:
What will be the primary use of the processor?
Each type of processor is designed with different goals in mind, from maximizing performance to minimizing power consumption, making the choice of the right processor highly dependent on the intended use. Here is a classification of the most common types:
- Desktop Processors: Designed for desktop computers. Optimized for performance and often consume more power than their mobile counterparts.
- Mobile Processors: Used in laptops and portable devices. Focused on energy efficiency to prolong battery life.
- Server Processors: Optimized for reliability and continuous performance, capable of handling multiple tasks and users simultaneously. Examples include Intel's Xeon processors and AMD's EPYC.
- Workstation Processors: Aimed at professionals who need high performance for tasks like 3D design, video editing, scientific calculations, etc. They are more powerful than desktop processors but less so than server processors.
- Embedded Processors: Used in embedded systems, where the processor is integrated into a device to perform specific functions (for example, in cars, home appliances, and IoT devices).
What should be the number of Cores and Threads of the Processor?
The number of cores in a processor is a crucial feature for multitasking. Nowadays, many modern programs are optimized to take advantage of multiple cores. Lower-end processors usually have 2 or 4 cores, while high-end ones can have 8, 12, or more.
- Multitasking: If you use several applications simultaneously or edit videos, the number of cores and threads is essential.
- Gaming: Although most games do not use more than 4 or 6 cores, some modern and future games will take advantage of higher-capacity processors.
What should be the frequency of the processor?
Clock frequency refers to the speed at which the processor executes instructions, measured in gigahertz (GHz). A higher clock speed means the processor can perform tasks faster, which is essential for demanding tasks like gaming or graphic design. Many modern processors can temporarily boost their frequency to handle higher loads (turbo frequency). This is important for short-term intensive tasks.
What should be the size of the processor's cache?
The processor's cache is ultra-fast memory that stores temporary data to accelerate repetitive operations. A larger cache size allows for faster performance, especially in high-demand applications like gaming, video editing, or engineering software. Common caches include L1, L2, and L3, with L3 being the largest and slowest but also the one that can store the most data.
Is the processor compatible with the motherboard and RAM?
Each processor is designed for a specific type of motherboard socket. For example, Intel processors typically use LGA sockets (LGA1200 for 10th Gen, LGA1700 for 12th Gen, etc.), while AMD Ryzen processors use the AM4 or AM5 socket. It's crucial to make sure that the motherboard you choose is compatible with the processor you're buying.
Additionally, the motherboard must support the type of RAM (DDR3, DDR4, DDR5, etc.) and the speeds of the RAM you want to use. RAM generations, such as DDR4 and DDR5, have different physical and voltage specifications. For example, a modern processor that supports DDR4 will not be compatible with DDR5 unless the motherboard supports both, which is rare.
To ensure optimal performance, it's essential to consider the RAM you'll be using. If you want to delve deeper into this topic, we recommend reading our article What Should You Know Before Buying RAM? There you'll find essential information on how to choose the right RAM and ensure the best compatibility with your processor and motherboard. Also, keep in mind that sometimes a BIOS/UEFI update can add support for new RAM or improve existing compatibility.
What is better: more cores or higher clock speed?
Deciding between more cores or a higher clock speed in a processor is not a choice of one being better than the other universally; rather, it depends on your specific needs. More cores are ideal for those who work with multiple applications simultaneously or use software designed for parallel processing. On the other hand, a higher clock speed benefits applications and games that have not been optimized for multiple cores or that depend on sequential processing speed. Older games, certain office applications, and tasks where latency is crucial, like some financial operations or web browsing, tend to run better when the processor has a high clock speed.
In summary, for tasks that benefit from parallelization, like creative content or software development, more cores could be the best option. While for tasks that depend on linear processing speed, or for users seeking maximum speed in less modern games or single-thread applications, a higher clock speed would be preferable. Also, consider the software you use most frequently and how it is optimized before making a decision.
What processor is best for gaming?
Choosing the best processor for gaming depends on your specific needs, budget, and other components of your system. The Intel Core i9 and Ryzen 9 are excellent options for gamers and content creators, while the Intel Core i5 and Ryzen 5 are more affordable and still provide solid performance for most modern games. Games that rely on single-core performance benefit from processors with higher clock speeds. The choice between these processors will depend on your budget, whether you already have an AMD or Intel platform (since motherboard and RAM compatibility can affect costs), and whether you are looking for the best performance in gaming or a balance between gaming and productivity applications.
Intel Processors
Intel is one of the most recognized processor manufacturers in the world, and its CPUs are widely used in a variety of devices, from laptops and desktops to high-performance servers. The Intel Core processor families (which include i3, i5, i7, and i9) stand out by offering solid performance for different types of users, from those who perform light tasks to gamers and professionals in jobs that require high processing power. It is important to understand their differences to choose the right option:

- Intel Core i3: It is ideal for users looking for a processor for basic tasks like web browsing and office software use. These processors typically have between 2 and 4 cores, and their speed is sufficient for most everyday activities.
- Intel Core i5: This processor is a step up, suitable for casual gamers and users who perform moderate multitasking. It offers between 4 and 6 cores and can be found in mid-range and high-end computers. With Turbo Boost technology, i5 processors can increase their clock speed when more power is needed, which is ideal for gaming and light content editing.
- Intel Core i7: For those who need higher performance, i7 processors are excellent options. With between 6 and 8 cores, they can handle demanding tasks like high-resolution video editing, 3D modeling, and AAA games with high requirements. They are also popular among content creators who require speed in intensive multitasking tasks.
- Intel Core i9: This is the highest range of Intel Core processors, aimed at professional content creators and demanding gamers. With more than 8 cores and extremely high clock speeds, these processors are the perfect choice for those needing the best performance in rendering, simulation, or video editing in 4K or 8K.
- Intel Xeon: Intel Xeon processors are specifically designed for workstations and servers, offering business-level performance and reliability. They are primarily used in environments where large amounts of processing power and stability under intensive loads are required. While Intel Xeon is not a common option for the average computer user, it is essential in corporate, scientific, and professional fields that demand high performance and reliability at scale.
What is Turbo Boost Technology?
Turbo Boost is another notable technology from Intel, which allows processors to increase their clock frequency above the base speed when applications require it. This is particularly useful for tasks that do not always require the full power of the processor but need a temporary boost, like when rendering a video or running an intensive video game for a few minutes.
What is the difference between Intel UHD and Iris Xe Graphics?
Intel UHD Graphics is suitable for basic daily use, such as browsing the internet and watching videos, offering sufficient graphic performance for these tasks. On the other hand, Intel Iris Xe Graphics significantly elevates the level with better performance in games and creative applications, thanks to its greater number of processing units and advanced technologies, making it ideal for those seeking a richer graphic experience without the need for a dedicated graphics card. Iris Xe is more aligned with current and future trends in integrated graphics, with better support for new technologies and graphic standards.
What is Hyper-Threading Technology?
Intel's Hyper-Threading technology allows processors to handle more tasks simultaneously by splitting each physical core into two virtual processing threads. This technology is present in many Intel processors, especially in the i7 and i9, enhancing performance in multitasking tasks and applications that require a high level of processing, such as video editing and live streaming.
AMD Processors
AMD processors have gained ground in recent years, offering a powerful alternative to Intel in various market segments, especially in gaming, workstations, and high-performance budget solutions. AMD has developed innovative technologies that have positioned it as one of the best options for those seeking excellent value for money without compromising performance. It is important to understand their differences to choose the right option:

- AMD Ryzen 3: This low-end processor is ideal for users with basic needs, like internet browsing, document editing, and basic multimedia use. With between 4 and 6 cores, it is an affordable option for entry-level PCs that need to handle everyday tasks efficiently.
- AMD Ryzen 5: Designed for users looking for a balance between price and performance. It offers between 6 and 12 cores, making it perfect for casual gaming, moderate video editing, and more intensive multitasking. Its multitasking performance improves significantly thanks to multi-threading technology.
- AMD Ryzen 7: With 8 to 16 cores, the Ryzen 7 is the preferred processor for those needing performance for tasks like 4K video editing, multimedia content creation, and advanced gaming. Its power allows smooth handling of professional applications and an uninterrupted gaming experience.
- AMD Ryzen 9: For those seeking the best in performance, the Ryzen 9 offers up to 16 cores and 32 threads, making it ideal for extreme gaming, professional workstations, and applications that require a high level of processing, such as simulation or graphic design. It is comparable to the Intel Core i9 series and surpasses many competitors in benchmarks.
- AMD Ryzen Threadripper: It is designed for professionals who require massive processing power, such as video editors, engineers, data scientists, and content creators. With a range of up to 64 cores and 128 threads, these processors are ideal for high-performance workstations. Their ability to handle multiple tasks simultaneously makes them an unprecedented option for heavy workloads such as 3D rendering, software compilation, and complex simulations.
What is Zen and Zen 4 Architecture?
One of the reasons behind the success of AMD processors is its Zen architecture. Since its introduction in 2017, the Zen architecture has significantly improved with each iteration, and the most advanced is currently Zen 4. This architecture uses a 5-nanometer manufacturing process, allowing for greater energy efficiency and an increase in performance compared to previous generations. Thanks to this architecture, AMD processors can offer more cores and better clock speeds while maintaining lower power consumption compared to their competitors.
What are AMD Radeon Integrated Graphics?
AMD also offers processors with integrated Radeon graphics through its APUs (Accelerated Processing Units). These units combine a CPU with high-performance integrated graphics, eliminating the need for a dedicated graphics card for users who do not require advanced graphics capabilities. Ryzen APUs with Radeon Graphics are perfect for budget computers that need to handle basic graphic tasks, light gaming, or video editing without requiring a dedicated GPU.
What is Ryzen Master for Overclocking?
One of the most attractive features of AMD Ryzen processors is the ease of overclocking. With the Ryzen Master tool, users can easily adjust the clock speeds of the processor to gain more performance without extra software or complex BIOS configurations. However, remember that overclocking should always be done with knowledge and care, ensuring that the system’s cooling is adequate to handle the increased temperature and power consumption.
What is the Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) Technology?
AMD's Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT) technology is similar to Intel's Hyper-Threading, allowing each physical core to handle two processing threads at the same time. This optimizes performance in tasks that require intensive CPU usage, such as video editing, rendering, and gaming. SMT is available in most Ryzen processors, making them a highly competitive option for multitasking tasks.
Where Can You Buy Processors in Latin America?
Buying processors in Latin America depends on the country you are in, as options vary in terms of availability, after-sales service, and prices. In some Latin American countries, certain models of processors may not be immediately available. Shopping at local stores like Pana Compu will ensure you have access to products that are in stock and can be delivered quickly.
Where to Buy Processors in Peru?
In Peru, you can find processors in physical stores, which offer a wide range of Intel and AMD options. These stores often have promotional offers and local warranties. Additionally, platforms like Pana Compu, which sells Processors in Peru, allow you to get fast shipping options on products that may not be available in physical stores. This is ideal as, being official sellers, they guarantee that warranties are valid throughout the country.
Where to Buy Processors in Panama?
In Panama, stores like Ciudad de Panamá are good options for acquiring processors, offering both Intel and AMD products, and Amazon can be a good option if you are willing to wait for longer shipping times, especially for the latest generation processors or exclusive models. However, Pana Compu is known for its variety of high-end hardware options and fast delivery products, so it is possible to find processors in Panama from newer generations and also older ones at more accessible prices in stores like Pana Compu.
In summary: What Should You Know Before Buying a Processor?
When you are in the market to buy a new processor, compatibility is the first aspect to consider. This includes ensuring that the CPU socket is compatible with your motherboard and that the chipset supports all the features of the processor you are interested in. The purpose of use is key to choosing the right processor. If your focus is gaming, a processor with a good combination of cores, threads, and clock speed, like AMD's Ryzen models or Intel's Core i7/i9, will provide you with the best performance.
Regarding cores and threads, think about your multitasking needs. Processors with more cores and support for technologies like Hyper-Threading or SMT will allow you to run heavy applications in parallel more efficiently. Consider the generation of the processor because even within the same series, newer generations tend to be more efficient and offer better performance per clock cycle. Lastly, if you are interested in overclocking, look for models that are unlocked for this practice, but also ensure you have adequate cooling solutions and a motherboard that supports overclocking to avoid stability issues or hardware damage.
Comments
All opinions are of our customers friends. Join the conversation!
No comments yet... Be the first!